Other recent blogs


Let's talk
Reach out, we'd love to hear from you!
The API testing market is projected to grow beyond $3.8 billion by 2026. Organizations deploying AI-first strategies are discovering that robust API testing frameworks are the key to the difference between digital innovation and system-wide failure. One misconfigured endpoint can cascade into security breaches, revenue loss, and broken user experiences across microservices architectures.
This guide examines the importance of API testing tools in ensuring quality assurance, identifies the frameworks that dominate the 2026 landscape, and provides guidance on selecting the right solution for your technical stack. We examine the top API testing tools available today, focusing on open-source and free options that deliver enterprise-grade capabilities without vendor lock-in.
What are API testing tools?
API testing tools are specialized software platforms designed to validate the functionality, performance, security, and reliability of application programming interfaces. These tools automate the process of sending requests to API endpoints, analyzing responses, and verifying that APIs behave as expected under various conditions.
Unlike GUI testing, which validates what users see, API testing operates at the integration layer. It examines how services communicate, exchange data, and handle errors before issues reach production environments. This approach identifies integration failures, data integrity issues, and security vulnerabilities that would be costly to rectify later in the development cycle.
Modern API testing tools support multiple protocols, including REST, SOAP, GraphQL, and gRPC. They provide features for functional validation, load testing, security scanning, and contract verification between microservices.
Why API testing matters in the quality assurance lifecycle?
APIs function as the connective tissue of modern software architectures. When an API fails, the failure propagates across dependent systems, resulting in cascading outages that negatively impact user experience and business operations. API testing delivers several critical advantages that justify its position as a core QA practice.
Early defect detection reduces costs substantially. Issues found at the API layer cost significantly less to fix than bugs discovered in production. Testing APIs before UI development begins allows teams to validate business logic and data flows when changes are still inexpensive to implement. Security vulnerabilities get identified before deployment, preventing costly breaches. APIs expose sensitive data and business functions to external systems, making them prime targets for attackers. Testing tools can identify authentication weaknesses, injection vulnerabilities, and authorization flaws that attackers could exploit. Security testing focuses on threats such as SQL injections, cross-site scripting, and broken authentication.
Performance bottlenecks surface under realistic load conditions through systematic testing. Load testing simulates production traffic patterns to identify response time degradation, memory leaks, and throughput limitations. Teams can optimize API performance based on concrete data rather than assumptions about how the system will behave at scale. Integration issues are often identified before system testing when multiple services interact through APIs. Integration testing verifies that contracts between systems remain valid, preventing situations where changes to one service break dependent applications without warning.
How API testing frameworks enable rigorous quality assurance?
API testing frameworks offer structured approaches for validating interfaces throughout the software development lifecycle. These frameworks differ from standalone tools by offering programmatic test creation, execution engines, and integration with development workflows. Frameworks support multiple testing methodologies including functional testing that validates endpoints return correct responses for given inputs, performance testing that evaluates response times and throughput under load, security testing that scans for vulnerabilities, and contract testing that ensures API providers and consumers maintain compatible expectations.
The frameworks integrate directly into CI/CD pipelines, enabling automated testing on every code commit. This continuous validation catches regressions immediately rather than waiting for manual QA cycles, while development teams receive fast feedback about code changes that allows them to address issues while context is fresh. Language-specific frameworks like REST-Assured for Java or Pytest for Python provide deep integration with existing codebases. These tools leverage familiar syntax and patterns, reducing the learning curve for development teams already working in those ecosystems.
Framework capabilities extend beyond simple request-response validation. Teams can define test scenarios using human-readable formats, implement data-driven testing, and create mock services for testing isolated components. Advanced frameworks support chaos engineering to test system resilience under failure.
What are the top 12 API testing tools dominating the 2026 industry?
The API testing landscape in 2026 features mature open-source projects and free tools that rival commercial offerings in capabilities.

Postman
Postman remains the most widely adopted API client for manual and automated testing. The platform provides a visual interface for constructing requests, managing collections, and executing test suites. Postman introduced features to test LLMs and use a visual, no-code canvas to build agents and configure multi-step workflows. The free tier supports basic testing needs, while paid plans add collaboration features and advanced monitoring capabilities.
SoapUI
SoapUI is an open-source API testing tool for REST and SOAP APIs that allows users to create automated functional, regression, and load tests. The tool offers a graphical interface that simplifies test creation, eliminating the need for programming expertise. SoapUI excels at creating mock services from WSDL files, enabling frontend testing before the backend implementation is complete.
Apache JMeter
JMeter originated as a performance testing tool but evolved into a comprehensive API testing solution. Apache JMeter is designed to test the performance of web applications, APIs, and network services by simulating heavy loads. The tool supports multiple protocols, provides extensive reporting capabilities, and integrates with CI/CD pipelines through command-line execution.
REST-Assured
REST-Assured is an open-source Java Domain-specific language that simplifies testing of REST services by eliminating boilerplate code. The framework allows developers to write API tests using readable syntax that integrates seamlessly with JUnit and TestNG. REST-Assured handles authentication, header management, and response validation through a fluent API.
Karate DSL
Karate DSL combines API test automation, performance testing, and API mocks into a single unified framework. The tool utilizes a behavior-driven development syntax that enables testers to write tests without prior programming knowledge. Karate supports data-driven testing, environment switching, and provides a built-in debugger for troubleshooting.
Insomnia
Insomnia offers a clean, minimalist interface for API testing with native GraphQL support. The tool provides fast request execution, environment variable management, and code generation capabilities. Insomnia's lightweight architecture handles large API suites efficiently, making it suitable for teams managing hundreds of endpoints.
Bruno
Bruno is an offline-first, open-source API client that stores collections in version-controllable files rather than relying on cloud sync. This approach gives teams full control over their API collections and enables seamless collaboration through Git workflows. Bruno challenges cloud-based tools by prioritizing local storage and privacy.
Hoppscotch
Hoppscotch is a free, open-source API request builder known for speed and minimalistic UI. The browser-based tool allows developers to send requests, inspect responses, and copy results without installing desktop applications. Hoppscotch serves as a lightweight Postman alternative for teams preferring browser-based workflows.
Taurus
Taurus simplifies performance and API testing by abstracting complex tools like JMeter, Gatling, and Locust using human-readable YAML files. Teams can define tests without heavy scripting, making Taurus popular for CI/CD-friendly automated performance testing. The framework supports multiple execution engines while providing unified reporting.
Playwright
Playwright provides cross-browser automation with robust API testing capabilities. The framework offers reliable automation with built-in test isolation, parallelism, and API testing support. Playwright handles modern web applications effectively and integrates well with JavaScript-based testing workflows.
Citrus Framework
Citrus is an open-source integration testing framework for message-based systems that provides a fluent Java DSL for defining automated interactions across HTTP, REST, SOAP, JMS, Kafka, and MQTT. The framework excels at testing complex integration scenarios where multiple protocols and messaging patterns interact.
Airborne
Airborne is a lightweight Ruby-based API automation framework built on RSpec. The framework provides a code-first workflow for teams preferring Ruby's expressive syntax. Airborne enables fast HTTP testing without GUI dependencies, making it suitable for developers who prefer command-line workflows.
How do you select the right API testing framework?
Choosing an API testing framework requires evaluating technical requirements, team capabilities, and operational constraints.
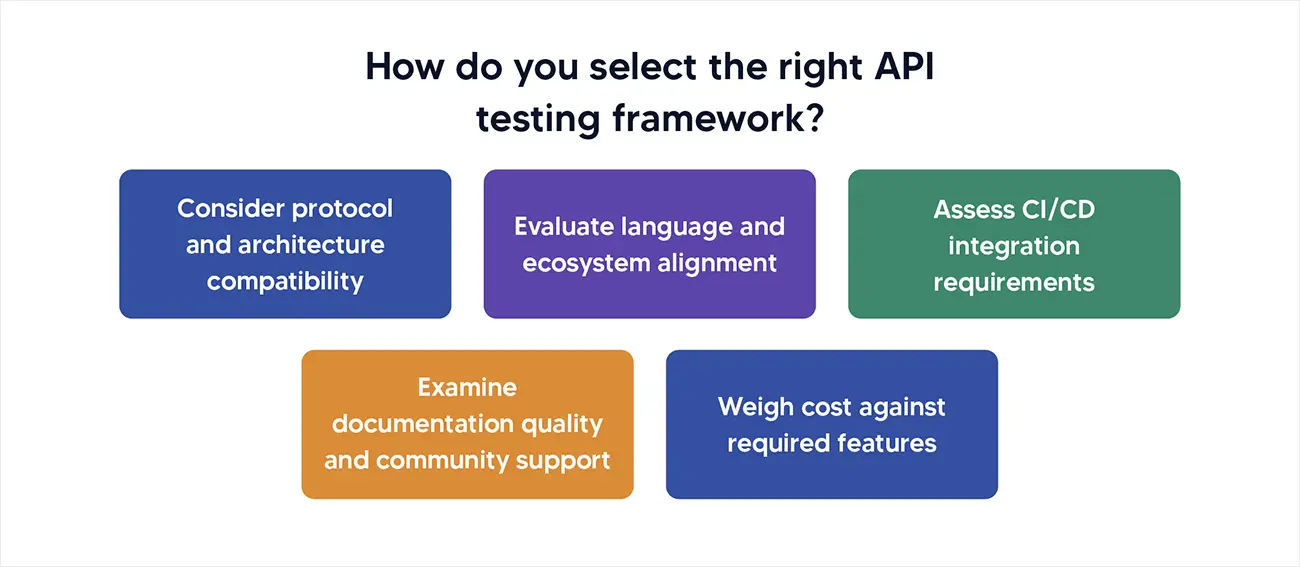
- Consider protocol and architecture compatibility
Verify that the framework supports the protocols your APIs use. REST APIs dominate modern architectures, but legacy systems may require SOAP support. Protocol support should include REST, SOAP, GraphQL, or gRPC based on your needs. GraphQL APIs need specialized tooling that understands schema introspection and query validation.
Microservices architectures benefit from frameworks that support contract testing. These tools validate that service boundaries remain stable as teams deploy changes independently. If your architecture includes message queues or event-driven patterns, select frameworks that can test asynchronous communication.
- Evaluate language and ecosystem alignment
Framework compatibility with your system and programming language makes integration into existing workflows easier and reduces the learning curve. Java teams gain productivity by using REST-Assured, which integrates with Maven, Gradle, and existing test runners. Python teams benefit from Pytest's extensive plugin ecosystem and familiar syntax.
Consider the existing skill sets within your QA and development teams. Frameworks requiring extensive programming knowledge may slow adoption if teams lack coding experience. Conversely, developer-heavy teams may prefer code-based frameworks over GUI tools.
- Assess CI/CD integration requirements
Look for frameworks that integrate seamlessly with your CI/CD pipeline to enable automated testing and consistent quality assurance. Command-line execution capability is essential for pipeline integration.
Frameworks should support environment variables, configuration files, and result reporting in formats that CI tools consume.
Evaluate whether the framework can run in containerized environments. Docker support enables consistent test execution across development, staging, and production environments. Cloud-native frameworks that run effectively in Kubernetes provide better scalability for large test suites.
- Examine documentation quality and community support
Robust documentation and strong community support make learning easier and help teams get assistance when needed. Active communities indicate ongoing development, timely security patches, and availability of third-party plugins. Check GitHub activity, Stack Overflow questions, and forum engagement before committing to a framework.
Documentation should cover common use cases, provide code examples, and explain integration patterns. Frameworks with poor documentation create adoption friction and increase time-to-value for testing initiatives.
- Weigh cost against required features
Open-source frameworks eliminate licensing costs but may require more setup and maintenance effort. Commercial tools provide polished interfaces and support contracts but introduce ongoing expenses.
Free tiers of commercial tools often suffice for small teams but impose limitations on collaboration features or test execution frequency.
Calculate total cost of ownership including training, maintenance, and infrastructure requirements. A free framework that requires significant custom development may cost more than a commercial solution with built-in features.
How Kellton accelerates API testing implementation
Organizations struggle with test data management challenges that slow API testing initiatives. Kellton's API testing services address these challenges by implementing proven frameworks and automation practices that accelerate quality assurance cycles.
Our teams bring expertise in selecting and implementing the right combination of open-source and commercial tools for your specific architecture. We establish testing frameworks that integrate seamlessly with existing CI/CD pipelines, enabling continuous validation without disrupting development workflows.
Kellton's approach emphasizes practical implementation over theoretical best practices. We configure test environments, create reusable test suites, and train internal teams to maintain testing infrastructure independently. This knowledge transfer ensures long-term success rather than creating dependency on external consultants.
Contact Kellton to discuss how our API testing services can reduce time-to-market while improving software quality across your technology portfolio.