Other recent blogs


Let's talk
Reach out, we'd love to hear from you!
Enterprises deploying AI agents at scale face an architectural crisis. While 40% of enterprise applications will integrate task-specific AI agents by the end of 2026, most technology environments were built for static processes, not dynamic intelligence. Current systems collapse under the load of AI agents issuing thousands of queries per minute. The gap between AI potential and operational reality has never been wider. Organizations report that only 2% have deployed agents at full scale, despite projections showing agentic AI could generate $450 billion in economic value by 2028.
This comprehensive guide examines enterprise agentic AI architecture: the structural foundation enabling AI agents to operate with autonomy, coordinate with other agents, and integrate seamlessly across enterprise systems. We explore proven design principles, the full technology stack, architectural blueprints, and real-world use cases to transform operations at scale. The shift from experimental pilots to production-grade autonomous systems marks a fundamental change in how organizations architect for intelligence.
What is enterprise agentic AI architecture and why does it matter?
Enterprise agentic AI architecture defines the structural framework that allows AI agents to operate autonomously while coordinating seamlessly with other agents, human workers, and enterprise systems. Traditional pipeline-based architectures fail here because agentic systems demand shared memory, orchestration layers, and real-time context flow to scale effectively.
The compounding advantage is clear. As agents learn and share insights across the organization, collective intelligence grows exponentially. Enterprise deployment requires governance built into the architecture from day one, ensuring every agent action remains traceable, explainable, and aligned with business goals through comprehensive lifecycle management.
Intelligent enterprise agentic AI architecture as the new execution layer
Modern enterprises operate across three distinct horizons of AI evolution, each building on the last:To support these transitions, organizations must align their underlying AI tech stack for 2026 to handle the shift from predictive analytics to trusted autonomy.
Horizon 1: Foundational intelligence
Organizations establish baseline automation through robotic process automation, business intelligence dashboards, and predictive analytics. These systems support human decision-making but require manual oversight and intervention. The focus is automating repetitive tasks and surfacing insights from historical data.
Horizon 2: Contextual intelligence
AI systems advance beyond simple automation to understand business context, user intent, and situational nuance. Natural language processing, recommendation engines, and adaptive workflows replace rigid rule-based systems. The shift moves from "if-then" logic to context-aware responses that adapt based on circumstances.
Horizon 3: Trusted autonomy
AI agents operate independently to plan, execute, and adapt to achieve defined business objectives. These systems run continuously, make decisions within approved boundaries, coordinate with other agents, and escalate only exceptions requiring human judgment. Agentic AI architecture becomes the execution layer driving this transformation, enabling true autonomous enterprise operations.
How does agentic architecture differ from traditional AI systems?
Traditional single-turn AI assistants respond to isolated prompts without context persistence or workflow execution. They function as reactive tools requiring constant human direction. Multi-agent AI architectures operate autonomously across complete workflows, maintain state across interactions, coordinate with other specialized agents, and learn from operational experience.
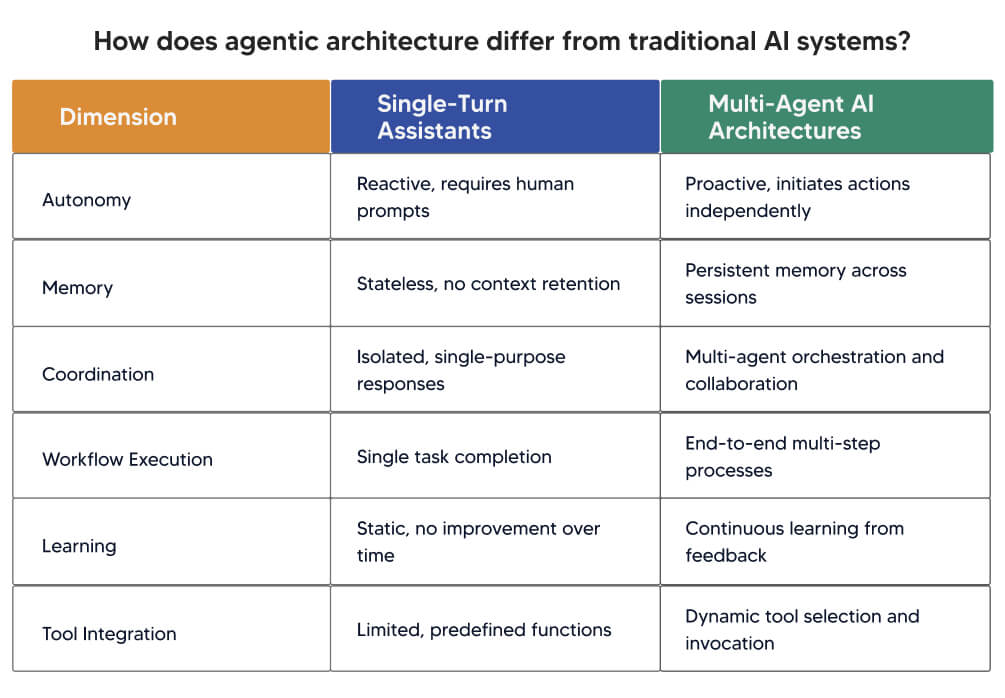
The transition from reactive tools to autonomous architectures represents a massive leap in technical complexity. Building these complex, multi-agent systems requires specialized generative AI development services to ensure the underlying reasoning engine is robust, scalable, and capable of high-stakes enterprise decision-making.
What are the foundational principles of enterprise agentic AI architecture?
Enterprise agentic AI architecture rests on four foundational pillars. Each addresses a critical requirement for deploying autonomous systems at scale.
- Bounded autonomy: Define clear decision boundaries
Agents need explicit operational limits that specify when they act independently versus when they escalate to humans. Enterprises implement graduated authority models where routine, low-risk decisions execute automatically, medium-risk actions trigger notifications, and high-stakes decisions require explicit approval before execution. Without these boundaries, agents either operate too conservatively (negating automation benefits) or too aggressively (creating compliance and operational risks).
- Contextual awareness: Ground decisions in enterprise data
Agents must access and integrate real-time enterprise knowledge to make informed decisions. This means connecting to CRMs, ERPs, policy repositories, knowledge bases, and operational systems. Grounding agent reasoning in verified enterprise data prevents hallucinations and ensures outputs reflect actual business context. Agents operating without proper grounding make confident but incorrect decisions that compound at scale, eroding trust and creating downstream problems.
- Orchestration and coordination: Enable multi-agent collaboration
Specialized agents working together outperform monolithic systems attempting everything. Task-specific agents focus on narrow domains (customer service, inventory management, compliance monitoring) while coordinator agents manage handoffs, resolve conflicts, and ensure workflow continuity. This modular approach scales efficiently because adding capabilities means deploying new specialized agents rather than rebuilding entire systems.
- Governance and explainability: Maintain trust through transparency
Every agent action requires comprehensive logging with traceable reasoning chains. Compliance teams must be able to see why an agent made specific decisions, what data it used, and which rules it applied. Organizations deploy governance agents that continuously monitor other AI systems for policy violations, bias, drift, or anomalous behavior. Security agents detect unusual patterns suggesting compromised systems or adversarial attacks. Without governance infrastructure, agentic systems become black boxes that enterprises cannot trust with consequential decisions.
What are the building blocks of the enterprise agentic AI architecture stack?
The enterprise agentic AI stack spans three tiers: engagement, capabilities, and data. Each tier contains specific layers essential for production deployment.
- Engagement tier
The interfaces layer provides connection points where AI services interact with users, whether customers, employees, or non-human systems. Emerging marketplaces and discovery APIs enable agent discovery and integration across partner companies. These platforms remain rudimentary but will mature as specialized vertical agents gain popularity.
Third-party agents represent autonomous systems that serve end-users efficiently. The business-to-AI agent category emerges as agents acquire purchasing capabilities within approved limits. This represents entirely new market space where AI agents themselves become customers for dedicated agentic services.
- Capabilities tier
The controls layer implements safeguarding mechanisms ensuring agents operate within policy boundaries. Security guardrails, compliance monitoring, and audit trail maintenance build trust and prevent misuse. Verification and policy compliance tools convert policies into rule sets cross-checked against model outputs, increasing confidence in autonomous task delegation.
The orchestration layer coordinates how AI agents work with each other and humans. It handles deployment, monitoring, and workflow management to maximize productivity while maintaining reliability. Fine-tuning capabilities adapt pre-trained models to specific enterprise contexts, enabling agents to develop rich specializations while collaborating effectively.
The intelligence layer provides AI reasoning and language capabilities from external providers or internal models. Organizations can accelerate deployment by leveraging a pre-integrated agentic AI platform that simplifies Agent Ops by monitoring, evaluating, and deploying agents at scale through structured lifecycle management.
The tools layer enables agents to interact with enterprise systems through secure API access or standard user interfaces. Next-generation RPA and process mining identify where to apply agentic AI by analyzing business processes and automating repetitive tasks with added reasoning capabilities.
- Data tier
The systems of record layer maintains enterprise memory and ensures continuity. It stores interaction histories, tracks decisions, and manages costs, enabling agents to learn from experience and contribute to long-term strategy. Agent workforce accounting tracks both direct costs and financial decisions made by autonomous systems as they gain expanded agency.
How should enterprises architect agentic AI integration?
The gateway integration model provides the comprehensive framework enterprises need for agentic AI deployment, balancing centralized governance with federated execution. This architecture delivers seamless integration, scalability, and security across the organization while maintaining flexibility for different business units and use cases.
GenAI applications form the user-facing layer, including retrieval-augmented generation systems, chatbots, and intelligent agents built with frameworks like CrewAI, LangGraph, or custom implementations. The AI gateway serves as the central orchestrator, managing all requests flowing through the system, enforcing guardrails, logging every interaction for audit purposes, providing centralized observability across deployments, and handling caching mechanisms to optimize performance and cost across all models. This centralization prevents the fragmentation that cripples many enterprise AI initiatives.
LLM fine-tuning and deployment capabilities leverage logs and user feedback to continuously improve large language models deployed for inference tasks. The architecture supports model and API integrations across various providers including OpenAI, Anthropic, AWS Bedrock, Azure, and self-hosted models, preventing vendor lock-in and enabling organizations to select optimal models for specific workloads. MCP servers and tools expose internal enterprise APIs through the Model Context Protocol, giving agents the ability to perform concrete tasks like updating CRM records, triggering workflows, or retrieving customer data. Agent-to-Agent protocols facilitate communication and coordination between multiple specialized agents, enabling collaborative workflows where different agents contribute their expertise to complex business processes.
Guardrails implementation occurs at two critical enforcement points. Input-layer guardrails filter requests before they reach the AI gateway, blocking obviously problematic queries and reducing unnecessary processing. Model invocation guardrails operate within or immediately after the gateway, validating outputs before they execute actions or return to users. This dual enforcement ensures both corporate-wide policies and agent-specific rules remain properly managed and controlled, with violations logged and escalated appropriately.
Omitting any component from this blueprint directly undermines scalability, reliability, and security. Without the AI gateway, organizations face fragmented governance where different teams implement inconsistent policies, broken authentication creating security vulnerabilities, and inability to enforce consistent guardrails across deployments. Missing MCP servers decouple agents from enterprise tools, transforming potentially powerful autonomous systems into isolated conversation engines unable to take meaningful action. Skipping guardrails opens the entire system to misuse, hallucinations, and unreliable outputs that erode stakeholder trust and create compliance exposure. Each component exists because production deployments proved its necessity.
What are the transformative use cases for enterprise agentic AI?
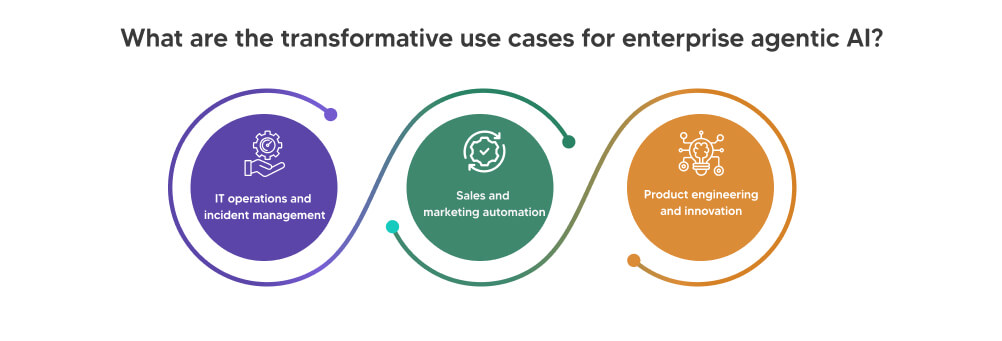
IT operations and incident management
Agentic AI systems monitor infrastructure, detect anomalies, diagnose issues, and implement resolutions autonomously. Organizations deploying these systems report significant reductions in mean time to resolution and service disruptions. Microsoft implemented agentic AI for cloud incident management, autonomously detecting service issues, analyzing root causes, and implementing fixes without human intervention.
The architecture integrates monitoring tools, AI agents analyzing collected data, incident management platforms, communication channels, and knowledge bases. Agents detect anomalies, diagnose root causes through log analysis, execute remediation actions, and update knowledge bases with new insights.
Sales and marketing automation
Agentic AI identifies high-intent leads, personalizes engagement strategies, and optimizes marketing performance through continuous learning. Organizations achieve higher conversion rates and improved customer experience while reducing operational overhead.
The system integrates customer data sources, AI agents performing lead scoring and segmentation, campaign platforms, lead intelligence tools, and communication systems. Salesforce Agentforce AI assists sales representatives by summarizing customer histories, suggesting talking points, and recommending negotiation strategies, improving lead follow-up efficiency by over 40%.
Product engineering and innovation
Agentic AI automates code generation, performs intelligent test orchestration, monitors deployment health, and generates insights feeding back into development processes. This results in faster release cycles, reduced errors, and improved product-market fit.
Morgan Stanley introduced DevGen.AI in January 2025, reviewing over 9 million lines of code and saving developers approximately 280,000 hours. The system automates legacy code modernization, allowing developers to focus on strategic initiatives rather than manual code translation.
Partner with Kellton for enterprise agentic AI architecture transformation
Kellton delivers end-to-end transformation capabilities spanning strategy, architecture, implementation, and optimization for enterprises adopting agentic AI. Our methodology accelerates time-to-value through proven frameworks and reusable assets. We integrate leading orchestration platforms with existing enterprise systems, configure specialized AI agents, and establish governance frameworks ensuring responsible deployment. Our teams provide change management support preparing organizations for orchestrated operations, including stakeholder engagement, training programs, and performance management system updates. Contact Kellton today to transform your enterprise with agentic AI architecture built for autonomous operations.
Frequently asked questions(FAQ)
Q1. What is the architecture of an agentic AI system?
Answer: Agentic AI architecture comprises three tiers: engagement (interfaces and third-party agents), capabilities (controls, orchestration, intelligence, and tools), and data (systems of record). This modular structure enables agents to perceive, reason, and act autonomously while maintaining coordination with humans and other systems.
Q2. What are the 7 layers of autonomous enterprise AI architecture?
Answer: The seven layers are: interfaces, third-party agents, controls, orchestration, intelligence, tools, and systems of record. Each layer serves specific functions from user interaction to governance, execution, and memory management, creating the complete infrastructure for autonomous operations.
Q3. What are the 4 characteristics of multi-agent AI architecture for enterprises?
Answer: The four key characteristics are bounded autonomy with clear operational limits, contextual awareness grounded in enterprise data, orchestration enabling agent collaboration, and governance ensuring explainability and compliance. These characteristics distinguish production-ready enterprise systems from experimental implementations.
Q4. What are key considerations for architecting your stack for the enterprise agentic AI era?
Answer: Key considerations include infrastructure readiness to support agent deployment, workforce training for human-AI collaboration, governance frameworks for ethics and compliance, security measures at input and invocation layers, integration with existing enterprise systems, and scalable orchestration platforms managing multi-agent coordination.
Q5. How do agentic AI frameworks power enterprise automation?
Answer: Agentic AI frameworks enable autonomous task execution through orchestration layers, memory management, and tool integration. They coordinate multiple specialized agents, maintain context across workflows, enforce guardrails, and integrate with enterprise systems. This architecture transforms isolated AI tools into collaborative autonomous systems that execute end-to-end business processes with minimal human intervention.
Q6. What are key benefits of using enterprise agentic AI architecture?
Answer: Enterprise agentic AI architecture delivers scalable automation, reduced operational costs, and faster decision-making. Organizations achieve 40-50% efficiency gains in targeted workflows, continuous 24/7 operations, compound learning effects as agents share insights, and consistent policy enforcement through built-in governance. The modular design enables rapid capability expansion without rebuilding existing systems.