Other recent blogs


Let's talk
Reach out, we'd love to hear from you!
As organizations accelerate AI adoption in 2026, test data management becomes critical for quality assurance teams facing unprecedented data complexity. Modern QA test data management requires synthetic datasets that mirror production accuracy while maintaining compliance across multiple jurisdictions. The challenge is no longer just managing test data—it's governing it at scale through test data management best practices that ensure security, consistency, and rapid provisioning.What is test data management Modern test data management practices when combined with intelligent automation tools become a critical infrastructure for QA teams navigating this landscape.
This blog examines QA test data management best practices and the tools that enable them. We explore how structured test data management transforms the software testing journey, from strategy formulation to implementation, helping teams maintain quality velocity without compromising data integrity or regulatory compliance.
Our QA experts help enterprises implement compliant, scalable test data strategies. Get a free assessment of your current TDM maturity.
Schedule Free ConsultationWhat is test data management and why does it matter?
Test data management is the systematic process of planning, designing, storing, and maintaining data used throughout software testing lifecycles. It encompasses creating realistic datasets, masking sensitive information, versioning test data, and ensuring availability across testing environments.
The practice addresses a fundamental QA challenge: production data contains real customer information that cannot be used directly in testing due to privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA. Simultaneously, tests require data that accurately represents production scenarios to validate functionality, performance, and security controls.
Organizations without formal test data management face predictable failures. Test environments contain outdated data that misses edge cases. Teams waste hours manually creating datasets. Security incidents occur when unmasked production data leaks through testing pipelines. Release cycles extend as teams wait for appropriate test data provisioning.
Research from Gartner indicates that poor data quality costs organizations an average of $12.9 million annually. Within QA operations, inadequate test data management directly impacts defect detection rates, testing coverage, and time to market.
Selecting the right test data management tools and implementing proven test data management best practices transforms QA operations from reactive to strategic.
Why is rigorous testing essential in data management for quality assurance?
Data-related defects during production of enterprise applications are common. These defects occur when applications process data combinations, volumes, or formats that were never validated during testing. Rigorous testing with representative data reduces this failure category significantly.
Consider financial services applications processing transactions. Testing with simplified datasets may validate basic functionality but miss scenarios involving currency conversion edge cases, duplicate transaction handling, or timezone-related calculation errors. These issues only surface when production data complexity exceeds test coverage.
Rigorous testing in data management serves multiple objectives beyond defect detection. It validates data migration accuracy when upgrading systems or consolidating platforms. It verifies that data masking and anonymization techniques preserve referential integrity while protecting privacy. It confirms that applications handle data volumes matching production loads without performance degradation.
Compliance requirements add another dimension. Regulations like SOC 2, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS mandate that test environments maintain equivalent security controls as production. Using unmasked production data in testing creates audit findings and potential breach exposure. Organizations need test data that is realistic enough for validation but sanitized enough for compliance.
The shift toward continuous delivery increases testing frequency, which amplifies data management importance. Teams running thousands of automated tests daily need reliable data provisioning that does not become a bottleneck. Poor test data management creates environment instability, causing false test failures that erode team confidence in automation.
What are the core test data management best practices for QA teams?
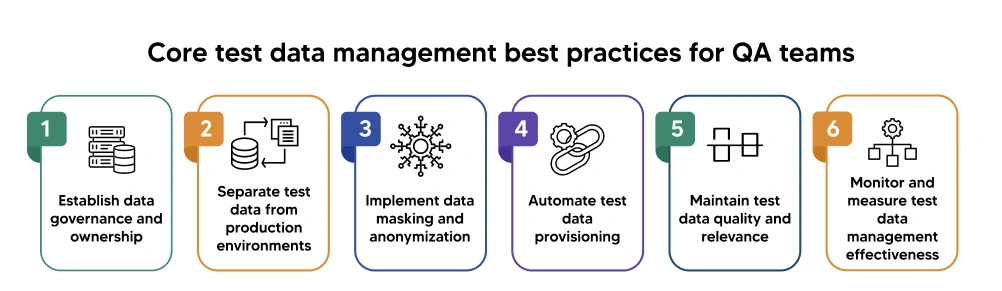
Establish data governance and ownership
Test data requires the same governance rigor as production data. Designate clear ownership for test datasets, defining who approves data creation, modification, and access. Create policies specifying data retention periods, refresh cycles, and disposal procedures.
Document data lineage tracking where test data originates and how it transforms through testing pipelines. This visibility helps teams understand data dependencies and impact when source systems change. It also supports compliance audits by demonstrating control over sensitive information throughout testing.
Implement access controls based on data sensitivity classification. Not all team members need access to all test data. Role-based permissions ensure developers testing front-end functionality do not access full datasets containing masked but recognizable patterns.
Separate test data from production environments
Physical and logical separation between production and test data prevents accidental data corruption and unauthorized access. Use distinct databases, schemas, or namespaces for testing activities. Network segmentation adds another protection layer, preventing test environments from directly querying production systems.
This separation extends to data synchronization processes. Automated pipelines that refresh test data should include masking and subsetting steps, never direct production copies. One-way data flows from production to testing prevent test data from accidentally migrating back to production environments.
Cloud environments offer infrastructure-level isolation through separate accounts or projects for production and non-production workloads. This architecture enforces separation through identity and access management policies rather than relying solely on application controls.
Implement data masking and anonymization
Data masking replaces sensitive information with realistic but fictional values. Effective masking maintains data format, type, and statistical properties while removing personally identifiable information. A masked email address retains valid email format. A masked credit card number passes validation algorithms but cannot process transactions.
Different masking techniques suit different scenarios. Static masking creates a one-time masked copy of production data for persistent test environments. Dynamic masking applies real-time masking when applications query databases, useful for production support teams needing to troubleshoot issues without accessing real customer data.
Subsetting reduces data volume by extracting representative samples from production datasets. A test environment might need only 10% of production data volume to validate functionality. Subsetting algorithms identify related records across tables, ensuring extracted subsets remain internally consistent.
Automate test data provisioning
Manual test data creation does not scale with modern delivery velocity. Automation provisions test environments on demand, reducing wait times from days to minutes. Self-service portals let developers and testers request pre-configured datasets matching specific test scenarios.
Infrastructure as code extends to test data. Version-controlled scripts define data creation, masking, and loading procedures. Teams apply the same change management discipline to test data pipelines as application code, tracking modifications and enabling rollback when issues arise.
Synthetic data generation offers an alternative to masked production data. Algorithms create artificial datasets matching production data patterns, distributions, and correlations. This approach eliminates production data dependencies entirely, useful for testing new features before production data exists or handling highly sensitive data categories.
Maintain test data quality and relevance
Test data degrades over time as applications evolve. Schema changes, new business rules, and updated integrations require corresponding test data updates. Establish regular reviews ensuring test datasets remain aligned with current production data characteristics.
Negative testing requires data that violates business rules and constraints. Maintain datasets specifically designed to trigger error handling, boundary conditions, and exception paths. These datasets are as important as positive test cases for comprehensive coverage.
Edge cases and rare scenarios need dedicated test data. Production datasets may not contain sufficient examples of uncommon situations that still require validation. Curate test data libraries covering low-frequency but high-impact scenarios like leap year processing, currency conversion extremes, or regulatory exception handling.
Monitor and measure test data management effectiveness
Establish metrics tracking test data management maturity. Measure time required to provision test environments. Track incidents caused by inadequate test data. Monitor test environment uptime and stability related to data availability.
Data coverage metrics indicate how well test data represents production diversity. Calculate percentages of distinct values, data combinations, and edge cases present in test datasets compared to production. Gaps in coverage highlight areas needing additional test data curation.
Compliance metrics demonstrate regulatory adherence. Track test environments containing unmasked production data, data access audit completion rates, and time to remediate data security findings. These metrics satisfy audit requirements and justify test data management investments.
Get our comprehensive 25-point checklist covering governance, security, automation, and compliance requirements.
Download Free ChecklistTop 10 Test Data Management Tools Compared (2026)
Selecting the right test data management tool depends on your technology stack, team size, compliance requirements, and budget. Based on our implementation experience across 200+ projects, here's a comprehensive comparison of leading TDM solutions.
| Tool | Best For | Key Strength | Deployment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Delphix | Enterprise, Database-Heavy | Data virtualization, subsetting | Cloud, On-prem |
| IBM InfoSphere Optim | Large enterprises, Mainframe | Legacy system support | On-prem, Private cloud |
| CA Test Data Manager | Mid to large enterprises | Integration with CA tools | Cloud, On-prem |
| GenRocket | Agile teams, Synthetic data | Synthetic data generation | Cloud, On-prem |
| K2View | Microservices, API testing | Entity-based TDM | Cloud-native |
| Informatica TDM | Data integration focus | ETL integration | Cloud, On-prem |
| Redgate SQL Provision | SQL Server environments | Developer-friendly | On-prem |
Detailed Tool Reviews
1. Delphix Test Data Management
Delphix dominates the enterprise TDM market with its data virtualization approach, creating virtual copies of production databases that consume minimal storage.
Key Features:
- Data virtualization:** Create unlimited virtual database copies from a single source
- Automated masking:** Policy-based masking with 40+ built-in algorithms
- Self-service provisioning:** Developers request environments via portal
- Compliance automation:** GDPR, CCPA, HIPAA masking templates
- API-first architecture:** Integrates with Jenkins, GitLab, Terraform
Best Use Cases:
- Large databases (500GB+) requiring multiple test environments
- Organizations with strict compliance requirements
- Teams practicing continuous integration/delivery
- Multi-cloud database deployments
Pros:
- Massive storage savings (90%+ reduction reported)
- Fastest environment provisioning (minutes vs. days)
- Strong compliance features
- Excellent Oracle, SQL Server, PostgreSQL support
Cons:
- High initial cost prohibitive for small teams
- Requires dedicated admin resources
- Learning curve for advanced features
- Limited NoSQL database support
2. IBM InfoSphere Optim
Overview: InfoSphere Optim remains the go-to solution for enterprises with mainframe systems and complex legacy architectures.
Key Features:
- Legacy system support: DB2, IMS, VSAM, and mainframe data
- Data archiving: Combines TDM with data lifecycle management
- Test data warehouse: Centralized repository for reusable datasets
- Advanced subsetting: Referential integrity-preserving algorithms
- Data comparison: Validate masked vs. production data quality
Pros:
- Unmatched mainframe data handling
- Proven in highly regulated industries
- Comprehensive data lifecycle capabilities
- Strong IBM ecosystem integration
Cons:
- Complex installation and configuration
- Dated user interface
- Expensive compared to modern alternatives
- Overkill for cloud-native applications
3. GenRocket
Overview: GenRocket specializes in synthetic test data generation, creating artificial datasets without production dependencies.
Key Features:
- Synthetic data generation: AI-powered realistic data creation
- Domain definitions: Reusable data models for different scenarios
- Real-time data streaming: Generate data on-demand via API
- Conditional logic: Complex business rule implementation
- Version control:** Git integration for data scenarios
Best Use Cases:
- New applications without production data
- Highly sensitive data (healthcare PHI, financial PII)
- Performance testing requiring large volumes
- Shift-left testing in agile environments
Pros:
- No production data dependency
- Unlimited data volume generation
- Excellent for greenfield projects
- Fast scenario creation
- Strong customer support
Cons:
- Initial domain modeling effort required
- May not capture production edge cases
- Limited data transformation capabilities
- Requires learning domain language
4. K2View
Overview: K2View's entity-based approach suits microservices architectures, creating micro-databases for each business entity.
Key Features:
- Entity-based TDM: Micro-databases per customer/entity
- Real-time data sync: Continuous updates from production
- API integration: GraphQL and REST interfaces
- Data privacy: GDPR "right to be forgotten" automation
- Multi-source aggregation: Combine data from multiple systems
Pros:
- Perfect for modern microservices
- Real-time data capabilities
- Built-in privacy compliance
- Scales horizontally
- Developer-friendly APIs
Cons:
- Requires significant architecture investment
- Not ideal for monolithic applications
- Smaller vendor with limited market presence
- Complex initial entity modeling
5. Redgate SQL Provision (formerly SQL Clone)
Overview: Developer-friendly TDM tool specifically for Microsoft SQL Server environments.
Key Features:
- SQL Server optimization: Native SQL Server integration
- Lightweight clones: Space-efficient database copies
- PowerShell automation: Scripting for CI/CD pipelines
- Simple masking: Built-in data masking capabilities
- SSMS integration: Works within SQL Server Management Studio
Pros:
- Extremely affordable
- Simple setup and learning curve
- Native SQL Server performance
- Excellent documentation
- Active user community
Cons:
- SQL Server only (no Oracle, PostgreSQL, MySQL)
- Limited masking compared to enterprise tools
- Basic reporting capabilities
- No centralized management for large teams
How do you implement a test data management strategy?
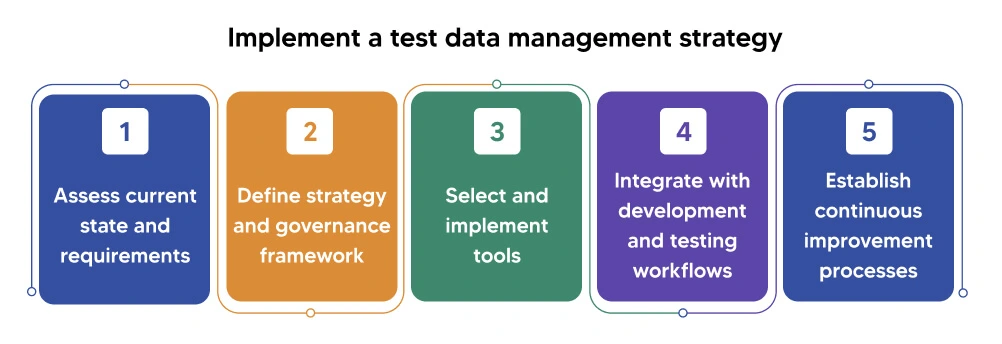
Following test data management best practices requires the right combination of process, governance, and test data management tools. Here's how to implement a comprehensive strategy.
Assess current state and requirements
Begin with a robust analysis of existing test data practices, tools, and pain points, followed by a detailed discussion with QA teams, developers, and operations staff to understand data needs across testing types including functional, performance, security, and integration testing. Documentation of test data sources is another step in identifying where test data originates, combined with the evaluation of compliance requirements applicable to your industry and geography. Privacy regulations dictate data handling requirements. Identify technical constraints, including database technologies, integration points, and infrastructure limitations.
Define strategy and governance framework
Create a test data management charter establishing goals, scope, and success criteria. It is a necessary step to define roles and responsibilities including data stewards, tool administrators, and end users. Next in the process comes establishing decision-making authority for data access requests, tool selection, and policy exceptions.
Develop policies covering data classification, masking requirements, access controls, retention periods, and disposal procedures. Policies should reference relevant regulations and explain compliance requirements in practical terms.
Select architecture patterns for test data infrastructure. Options include centralized test data repositories serving multiple teams, federated models where teams manage their own data with shared governance, or hybrid approaches balancing autonomy with control.
Select and implement tools
Evaluate test data management tools against requirements including data masking capabilities, subsetting algorithms, synthetic data generation, provisioning automation, and integration with existing CI/CD pipelines.
Many data management tools and open-source alternatives are available for subsetting, anonymization, and custom scripting with tools like Python Faker library suit organizations preferring build-over-buy approaches or having specific requirements commercial tools do not address.
Implementation should follow phased rollout starting with pilot projects demonstrating value before enterprise-wide deployment. Select initial use cases with clear pain points and measurable outcomes. Success with pilots builds organizational support for broader adoption.
Integrate with development and testing workflows
Test data management integrates into existing development workflows rather than operating as separate processes. Embed data provisioning into CI/CD pipelines so automated tests always run against fresh, appropriate datasets.
Service virtualization complements test data management by simulating dependent systems. Combined, these practices enable isolated testing without dependencies on external data sources or system availability.
Shift-left testing principles apply to test data management. Involve QA teams in data planning during requirements and design phases rather than addressing data needs only during test execution. Early planning identifies data requirements before development begins.
Collaboration between development, QA, and operations teams ensures test data management supports all stakeholders. Developers need data for unit testing. QA teams require comprehensive datasets for functional and regression testing. Operations teams use production-like data for performance and scalability testing.
Establish continuous improvement processes
Regular retrospectives identify test data management pain points and opportunities for improvement. Collect feedback from teams using test data to understand what works well and what needs refinement.
Stay current with evolving regulations affecting data handling. Privacy laws continue expanding globally, requiring ongoing compliance assessment. New regulations may necessitate policy updates or additional masking techniques.
Technology evolution brings new capabilities and challenges. Cloud adoption, containerization, and microservices architectures change how test data is stored and accessed. API-first architectures require different test data patterns than monolithic applications.
Benchmark against industry practices through conferences, user groups, and vendor communities. Learning how peer organizations address similar challenges accelerates maturity and prevents reinventing solutions.
How Kellton solves test data management challenges?
Kellton's software testing services implement comprehensive test data management strategies tailored to enterprise complexity. Our approach combines the best practices and tools discussed above with deep industry expertise across financial services, healthcare, retail, and technology sectors.
We assess your current test data landscape, identify compliance gaps and efficiency bottlenecks, then design governance frameworks aligned with your risk tolerance and delivery velocity requirements. Our implementation services include tool selection and configuration, data masking and subsetting pipeline development, and integration with your existing CI/CD infrastructure.
Kellton's QA teams bring two decades of testing experience to test data management challenges. We understand that effective test data management requires balancing competing demands: data that is realistic enough for meaningful validation, sanitized enough for regulatory compliance, and available quickly enough to support continuous delivery.
Partner with Kellton to transform test data from a testing bottleneck into a strategic advantage, enabling faster releases without compromising quality or security.
References:
1. Gartner Report: Data Quality: Best Practices for Accurate Insights